You would know that they routinely shed hair, sometimes a lot, depending on the season if you own a dog.
So, do be alarmed when your couch, carpet, and clothes have amassed a lot of animal fur.
Many dog breeds, Belgian Sheepdog, Bouvier des Flandres, and an Alaskan malamute, shed more hair than other breeds, confusing the new pet owners about whether their dog is suffering from a hair loss disease; however, it is routine!
However, it can be alarming if hair loss is accompanied by frequent scratchings, random bald patches, and other unusual signs. It often means an underlying medical problem is associated with hair loss or alopecia.
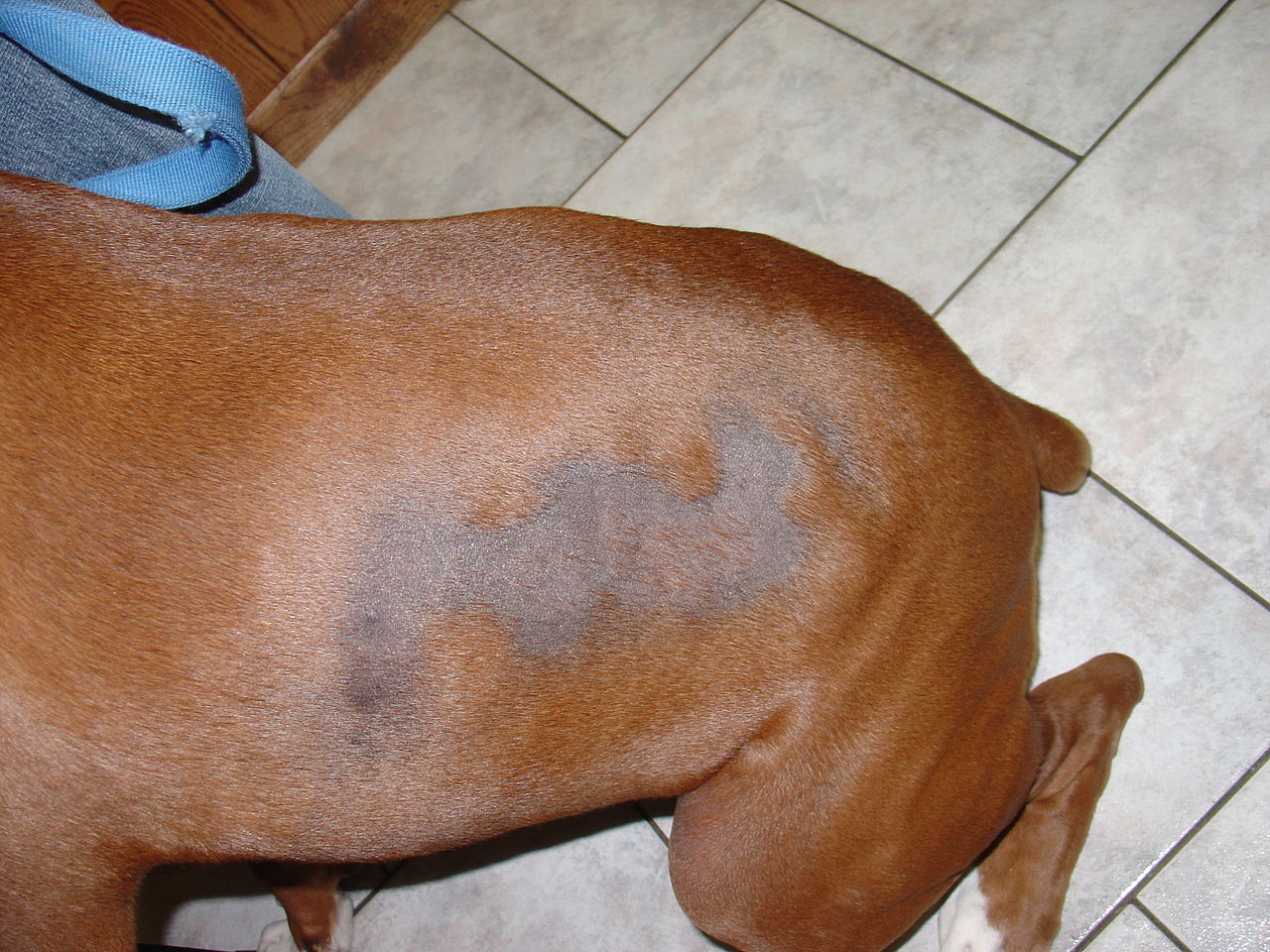
Stress, allergies, parasitic infection, and Cushing's disease are often the significant causes of alopecia in canines. Also shared in humans, it is a disorder that causes random bald patches and sometimes complete hair loss.
There are many reasons for sudden hair loss in dogs, so it’s often difficult to pinpoint a single cause. We recommend taking your dog to the vet as soon as you notice unusual signs.
Read on to find out the signs of hair loss in dogs and how to treat it on time.
Top Reasons for Hair Loss in Dogs
There are many reasons for hair loss in dogs. Sometimes it is congenital; other times, it may be a disease or an underlying medical condition.
A few of the most common reasons for canine hair loss are as follows:
1. Seasonal Shedding
Don't confuse seasonal shedding with allergies or medical problems.
Sometimes dogs can start losing a lot of hair mass when the weather turns warm, or the individual hair follicles become old and damaged.
Many dogs shed year-round, while others may shed in a particular season. Seasonal shedding is common during summer to help dogs' skin breathe easily.

Regular grooming ensures that your dog doesn't shed excessively because of hair follicle damage and hair mats. Moving your dog to a moderate climate can also reduce seasonal shedding.
2. Allergies
Dog allergy is one of the common causes of canine hair loss. Flea allergies, Atopy, and food allergies are common instigators of excessive hair loss.
Although flea allergy and atopy don't necessarily cause shedding, excessive scratching, biting, and licking because of the allergy can cause sudden hair loss.

Hair loss from allergies is an acquired problem.
- Atopy allergy is acquired from environmental irritants like pollen, mold, and dust mites.
- Flea allergy is acquired from flea infestation when your dog plays in the backyard or other infected animals.
- Many dogs are allergic to a particular food such as beef, dairy, wheat, corn, soy, etc. It's best to avoid feeding allergy-inducing food to your dog.
You can notice canine allergy when your dog is constantly scratching and biting the skin or when it shows signs of irritated, red areas on the skin.
The prescribed medications and dietary changes can quickly treat allergies in dogs.
3. Cushing's Disease
Hyperadrenocorticism, better known as Cushing's disease, is a condition caused by the prolonged exposure of the body’s tissue to excessive hormone cortisol levels.
Dogs that have been overfed with corticosteroid drugs can contract Cushing's disease. However, it is more common in dogs six years or older.
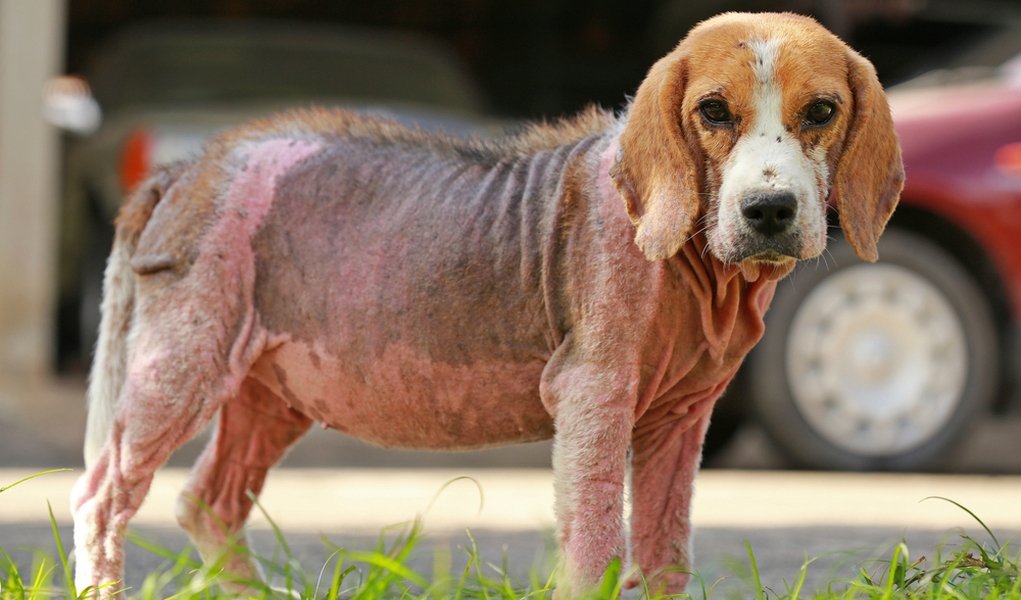

Cushing disease's symptoms include:
- Increased frequency of eating, drinking, and urinating
- Potbellied or bloated like appearance
- Less energy
- Insomnia
- Obesity
Your vet can better diagnose the disease by running different tests to recommend the best course of action for treatment.
4. Mange and Parasites
Mange is a skin disease common in dogs, birds, and reptiles, caused by microscopic parasitic mites that live on the surface of the skin and hair follicles.
Mange infection is caused by mites, like scabies mites and red mange that can burrow into the skin and can cause itching and massive hair loss.
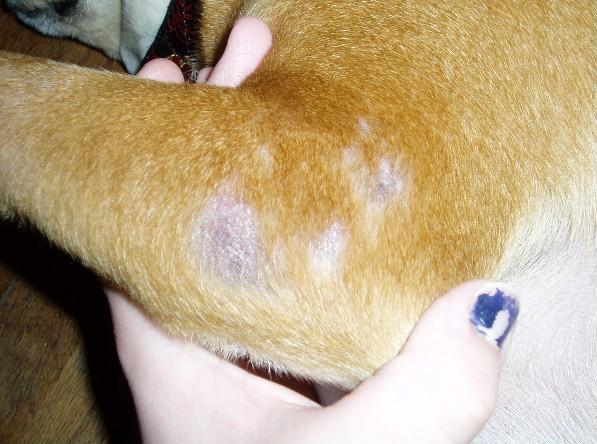
There are two significant forms of mange prevalent in canines, each caused by different mites:
- Sarcoptes scabies causes sarcoptic mange (also known as scabies). It's highly contagious and can easily pass from one dog to another. The symptoms include extreme itchiness, redness and rash, thick yellow crusts, and hair loss.
- Demodectic Mange (also known as red mange or Demodex) is caused by a cigar-shaped mite called DemodexCanis. They're ever-present in the body but harmless. It may attack dogs with a weakened immune system.
5. Bacterial and Fungal Infections
Bacterial and fungal infections can cause severe skin itchiness, hair loss, redness, and odor.
Look out for hair loss patterns around ears, stomach, chest, and eyes to conclude bacterial or fungal infection in dogs.
Common types of pathogenic bacteria in dogs include:
- Salmonella
- Leptospirosis
- Campylobacter
- Helicobacter
- Streptococcus
- Clostridia
- Bordetella
- E Coli
Dogs infected with ringworm also shed hair. Unlike other infections, ringworm causes circular or irregular hair loss. When you notice itchy or scaly patches, it's time to take your dog to the veterinarian.
After a complete examination, your veterinarian will advise the future course of action. Severe infections may require the use of antifungal shampoos, topical treatment, and drugs.
6. Underlying Medical Conditions
The underlying medical condition can also cause massive hair fall in dogs.
Pressure sores, trauma, abnormality in the growth of the hair shaft, thyroid disorder, sex hormone imbalance, and skin cancer are a few of the common causes of hair loss in dogs.

Identifying underlying medical conditions may include blood profile (blood testing), biopsy (determine skin cancer or tumor), skin impression smears (bacterial identification), etc.
Your veterinarian will administer antibiotics, antifungals, steroids, immunosuppressive drugs or Anti-cytokine drugs, and immunotherapy for the treatment depending on the medical condition.

Treatment of Hair Loss in Dogs
Here is the list of treatments available for canine hair loss.
|
Treatment
|
Specification
|
|
Antibiotics
|
Trilostane or other oral or topical antibiotics
|
|
Antifungals
|
Oral or topical treatment for yeat and ringworm
|
|
Steroids
|
It helps to treat skin conditions
|
|
Immunosuppressive Drugs
|
Environmental allergy (Atopy) control
|
|
Immunotherapy
|
It is administered orally or by injection
|
|
Behavioral medications
|
To control nervous chewing or licking
|
|
Medicated shampoos
|
To treat mange, allergies, and rashes
|
|
Hypoallergenic diets
|
To eliminate problematic food diets that may be causing allergy
|
|
Monthly flea preventative
|
To treat seasonal flea and tick problems
|
|
Thyroid medication
|
To reverse hair loss due to hormonal disorder.
|
|
Vitamin E, Vitamin A, and fish oil supplements
|
To treat the certain conditions or a predisposition to dry skin
|
|
An Elizabethan collar
|
To prevent your dog from licking or itching the affected site
|
|
Surgery
|
To remove sections of skin cancer or tumors.
|
Prevention of Hair Loss in Dogs
You can stop dogs' hair loss and skin problems by adopting preventive measures.
1. Reducing Shedding through Nutrition
Here is how to reduce canine shedding through selective nutrition and diet.
Feed your dog a high-quality diet
A healthy diet is a precursor to a healthy and thick coat in dogs. Be careful about using cheap can foods and home-prepared meals that usually lack nutrition. A high-quality diet contains all the essential nutrients, including Vitamin D, folic acid, and zinc, which help keep the dog's immune system strong.
Add Olive Oil or Flaxseed oil to dog food
One teaspoon (5 mL) per 10 pounds (4.5 kg) of body weight is an excellent place to start. These oils contain omega-3 fatty acids that help calm inflamed skin, decrease dandruff, and improve overall coat texture.
Give your dog occasional "human food"
Occasionally feed your dog human food such as fruits (apples and bananas), cucumbers, and cooked lean meat. However, be careful about providing food items such as chocolate, avocado, grapes, milk products, and onion.

2. Reducing Shedding through Grooming
Regular grooming is as essential as a dog’s daily diet and exercise. Over time, the dog’s coat gets tangled to create mats which can be a painful experience. An unkempt coat causes frequent and constant itching and scratches. Constant licking can cause excessive shedding. Grooming will help remove excess and lose fur and redistribute your dog’s skin oils into its fur.
Use de-shedding tools before the spring season when the dog’s coat begins to fall off. Consider bathing them with dog shampoo made for flea and tick control.

Conclusion
Hair loss in dogs is more common than you may imagine.
Therefore, it is essential to learn about canine hair loss and how to diagnose and treat it on time to ensure a happy life.
Get in touch with Urban Pet Hospital & Resort, the best doggy daycare in Urbandale, to learn more about dog shedding and preventive measures.