Did You Know? Urban slums have the highest cases of zoonotic infection. Most of the zoonotic diseases are caused by pet animals such as dogs, cats, rabbits, and horses.
Scientists in the US estimate that more than 6 out of every 10 known infectious diseases in humans are spread from animals, and 3 out of every 4 new or emerging infectious diseases in humans spread from animals.
What is Zoonotic Disease?
Zoonotic disease or zoonoses are terms used to describe an infection or disease that can be transmitted from an animal to a human being. In general, these diseases normally exist in animals but can affect humans through different forms of contact.
The zoonotic disease can be caused by a range of pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Of 1,415 pathogens known to infect humans, 61% are zoonotic in nature.
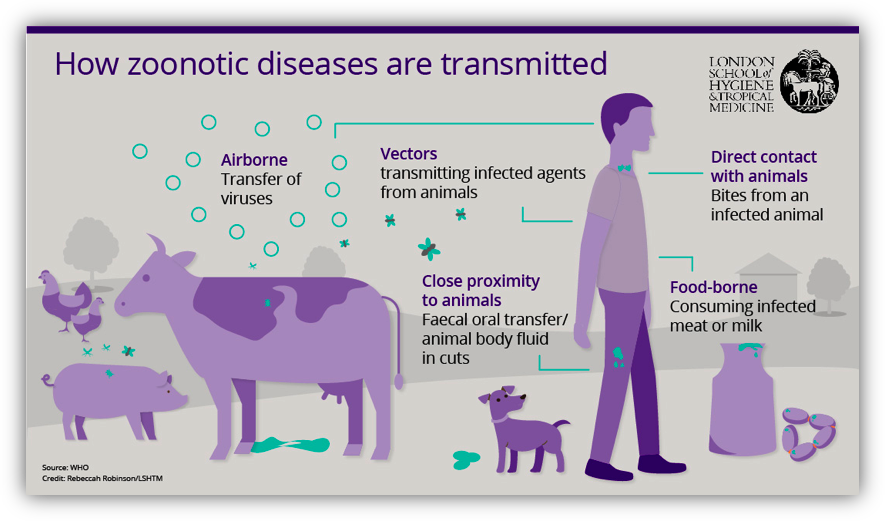
How is the Zoonotic Disease Transmitted to humans?
Zoonotic diseases can be transmitted from animals to humans through four major channels.
i. Direct contact
In the direct zoonosis, the disease is directly transmitted from animals to humans through media such as air (influenza) or through bites and saliva (rabies). Zoonosis can also occur from contact with blood, urine, mucus, feces, or other body fluids of an infected animal. Petting or touching an animal, and scratches can also account for zoonosis through direct contact.
ii. Indirect contact
In Indirect contact, the zoonosis takes place through a secondary medium with any direct contact with the infected animals. This can occur at places or areas where animals live and roam, or objects or surfaces that they were in contact with. Indirect contact can occur from pet habitats, animal shelter, and contaminated pet food or utensils.
iii. Vector-borne
Vector-borne diseases are transmitted by vectors such as mosquitos, fleas, and ticks. The vectors become a host for infection after they have bitten the infected animals. Then they are carried to human beings through the bite.
iv. Foodborne
Consuming contaminated food is another major concern for zoonotic disease. Although foodborne diseases are more common in third world countries, every year one in six Americans gets sick from eating contaminated food. Unpasteurized milk, undercooked meat or eggs, or raw fruits and stale vegetables can cause foodborne zoonotic diseases.
Who is more prone to Zoonotic Diseases?
Some people are more at risk of zoonotic diseases than others. The fitness, age, and medical condition of a person may determine the chances of transmitting zoonotic disease.
These groups of people include:
- Children younger than 5
- Adults older than 65
- People with weakened immune systems
The risk may be slightly higher in people with a compromised immune system from disease or medication which includes;
- people with AIDS/HIV.
- people on chemotherapy or receiving radiation therapy.
- people who are elderly or have chronic diseases.
- people with congenital immune deficiencies.
- people who have received organ or bone marrow transplants.
- pregnant women (the fetal immune system is not fully developed, and the pregnant woman's immune system is altered during pregnancy).
People who fall into these categories must be extra careful when they are around animals. Take basic precautions such as washing hands after petting or touching the animal, and avoiding secondary contacts such as staying away from contaminated food or pet shelters.
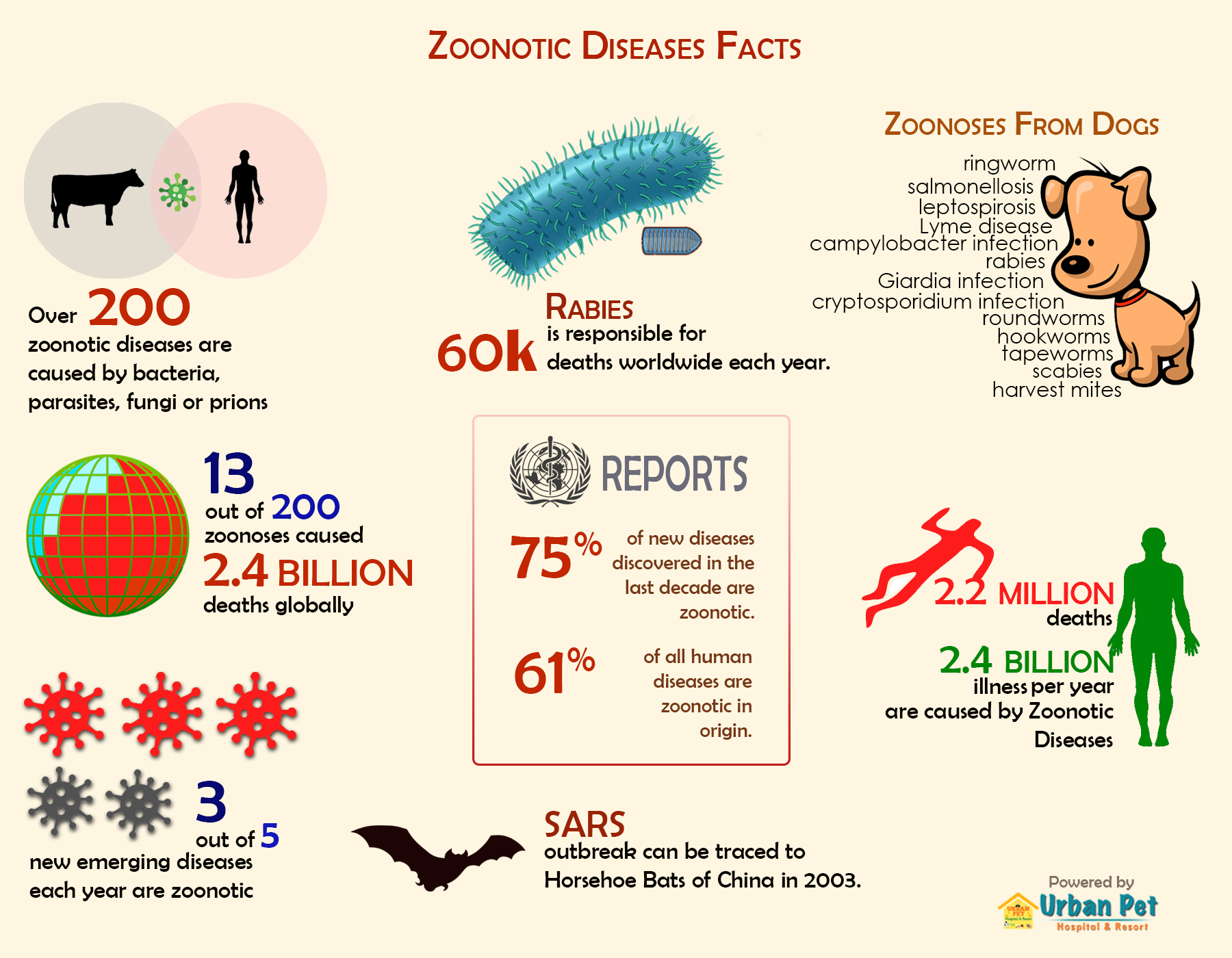
What Zoonotic Diseases does a Dog Carry?
Most of the zoonotic diseases in humans are transmitted from pet animals such as dogs, cats, rabbits, and horses.
According to the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), these are the most common zoonotic diseases found in the US. These can be prevented by implementing the best doggy daycare in Des Moines.
a. Ringworm
The symptoms of ringworm in dogs include dandruff-like scaling in the depths of the coat, red lesions on the head, chest, forelegs and the ridge of the back.
b. Salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is a symptomatic infection caused by bacteria of the Salmonella type. It usually results in symptoms like vomiting and diarrhea in dogs.
c. Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes inflammation of the brain in humans and animals. It is transmitted from infected animals to humans through bite or saliva. Rabies vaccination is the best way to avoid rabies infection in the future.
d. Leptospirosis
A leptospirosis is a common form of infection in dogs that is caused by corkscrew-shaped bacteria called Leptospira. Signs of leptospirosis include fever, lethargy, and lack of appetite.
e. Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is an infectious disease caused by the Borrelia bacterium which is spread by ticks. Lyme disease can cause kidney failure and death in severe cases.
f. Campylobacter infection
PetMD reports that up to 49 percent of dogs carry campylobacteriosis, shedding it into their feces for other animals to contract. Humans can easily contract the disease if they fail to practice proper hygiene after coming into contact with an infected animal. The signs of Campylobacter infection in dogs include watery to mucoid diarrhea, abdominal cramping or pain, lethargy, and fever.
g. Roundworms
Roundworms can infest the dog digestive tract. The signs of roundworm in dogs include colic, lethargy, vomiting, abdominal swelling, abnormal feces, etc. Coming in contact with contaminated soil or infected dog feces can result in human ingestion and infection.
h. Scabies
Sarcoptic mange or Scabies in dogs is caused by the Sarcoptes scabies mite, a highly contagious skin parasite. The mites burrow into their skin and cause severe itching that can result in the formation of scabs and hair loss.
Prevention from Zoonotic Diseases
Zoonotic diseases are reported to be one of the most common diseases contracted by humans worldwide. To prevent zoonotic diseases, you should adopt the following measures.
PERSONAL HYGIENE
- Wash hands before and after handling or petting animals.
- Avoid eating or drinking anything close to the pet’s shelter.
- Wear preventive overalls when handling farm animals.
- Avoid handling sick animals or animals with lesions without wearing any gloves and masks.
- Always wear a mask while entering pet shelters such as dog kennel and animal farms.
- DO NOT enter the agricultural animal facilities when you are sick!
- Use preventive gear while cleaning any animal area.
- If you notice any sign of illness, contact your medical personnel ASAP.
ENVIRONMENTAL MAINTENANCE
- Keep animal shelters such as kennel and cattle farm organized and regularly cleaned.
- It’s important to clean any urine and fecal build-up. Dry feces result in fecal dust which may be inhaled. Most bacteria reside inside the fecal build-up.
- Clean rooms have a lower likelihood of horizontal or zoonotic transfer.
- Build animal housing areas away from the house or in an isolated area unless you’re building a dog kennel.
- Quarantine the animal’s housing area with the help of experts when you notice the sign of any major infection or diseases.
HERD/FLOCK MAINTENANCE
This is more applicable if you own or handle a large number of animals such as cattle flock.
- Observe animals for health status on a daily basis.
- Report sick or dead animals.
- Note health problems such as diarrhea, difficulty breathing, depressed, immobile.
- Take extra caution in cleaning the areas around ill animals. Don’t spread possible pathogens.
- Isolate affected animals as appropriate.
- Record history or progression of animal disease.
Preventive Takeaways from Urban Pet Hospital and Resort
Urban Pet Hospital and Resort is a premier Doggy daycare in Urbandale that ensures the prevention of any infection or disease caused by animals. Here are four preventive takeaways that you should always keep in mind.
- Properly wash fruits and vegetables before consuming them.
- Prevent contamination of water sources.
- Undertake pet vaccinations.
- Avoid contact with wild animals.